Table of Contents
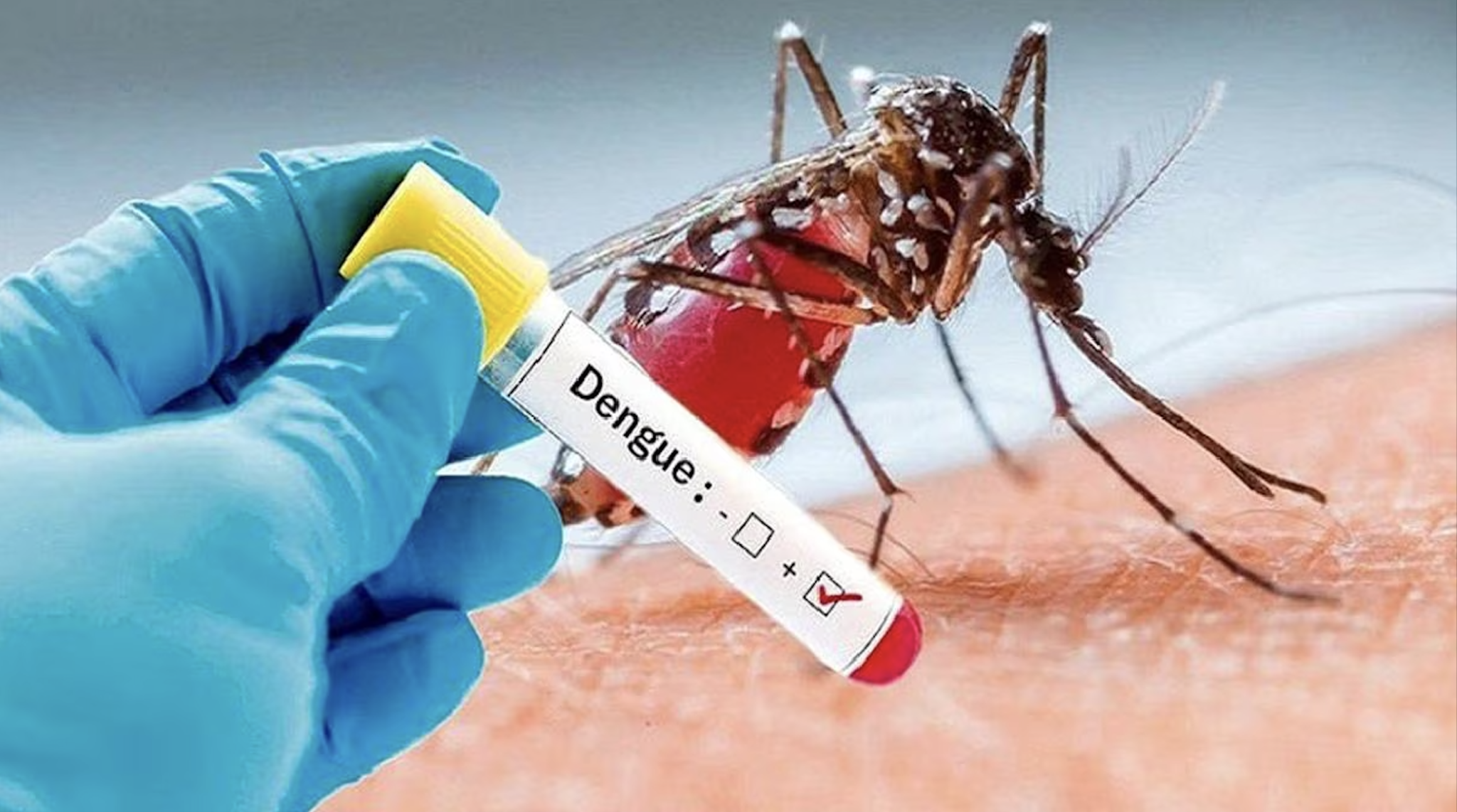
Dengue is one of the fastest-spreading mosquito-borne diseases in the world. It is common in tropical and subtropical countries, especially during the rainy season. What makes dengue dangerous is that it can quickly progress from a normal fever to a life-threatening illness if ignored. Knowing its causes, symptoms, and preventive steps is the best way to stay safe.
Causes/Risk Factors
Dengue is caused by the bite of the Aedes aegypti mosquito, which usually bites during the day. These mosquitoes breed in stagnant water found in open containers, old tires, or uncovered tanks. People living in densely populated or poorly maintained areas are at a higher risk of catching the disease, especially during monsoons when breeding conditions are ideal.
Symptoms/Signs
The first sign of dengue is usually a sudden, high fever. Along with this, people may experience severe headaches, pain behind the eyes, and extreme muscle and joint pain—which is why dengue is sometimes called “breakbone fever.” Skin rashes, nausea, vomiting, and weakness are also common. In severe cases, patients may notice bleeding gums or nosebleeds due to a drop in platelet count.
| Myths | Facts |
|---|---|
| Dengue spreads directly from one person to another. | Dengue only spreads through the bite of an infected Aedes mosquito. |
| Only dirty water breeds mosquitoes. | Aedes mosquitoes breed in clean stagnant water like tanks, pots, and buckets. |
| Dengue always causes death. | Most dengue cases are treatable with proper care if diagnosed early. |
| Papaya leaf juice is a cure for dengue. | No scientific cure exists — papaya leaves may support immunity but are not a treatment. |
Prevention
The best way to prevent dengue is by controlling mosquito breeding. Make sure there is no stagnant water around your home. Always cover water storage containers, change the water in flowerpots regularly, and dispose of items where water can collect. Use mosquito repellents, sleep under nets, and wear long-sleeved clothing, especially during the day. Community participation in fogging and cleanliness drives also helps reduce the spread.
📌 Case Study / Real-Life Example In 2023,
Pune reported over 10,000 dengue cases during the monsoon season. Most cases were linked to waterlogging in residential areas and uncovered water storage. After municipal authorities conducted awareness campaigns and households started covering tanks and removing stagnant water, the number of cases dropped significantly. This shows how simple preventive measures can save thousands of lives
Treatment/Cure
There is no direct cure for dengue. Treatment mainly focuses on relieving symptoms and preventing complications. Patients should drink plenty of fluids to avoid dehydration and take paracetamol to reduce fever and pain. Medicines like aspirin or ibuprofen should be avoided, as they can increase the risk of bleeding. In severe cases, hospitalization is needed to monitor platelet levels and provide proper care.
| ✅ Dos | ❌ Don’ts |
|---|---|
| Drink plenty of fluids to prevent dehydration. | Do not take aspirin or ibuprofen as they may increase bleeding. |
| Use mosquito repellents and nets. | Do not take aspirin or ibuprofen, as they may increase bleeding. |
| Visit a doctor if symptoms appear. | Don’t self-medicate with strong painkillers. |
| Keep surroundings clean and free of stagnant water. | Don’t leave water containers uncovered. |
Conclusion
Dengue may sound scary, but it is largely preventable with small steps like keeping our surroundings clean and avoiding mosquito bites. Early recognition of symptoms and timely medical care can save lives. Awareness is the first and strongest weapon against dengue.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Dengue
Q1. Can dengue spread directly from one person to another?
👉 No, dengue does not spread by touching, sharing food, or breathing near an infected person. It only spreads through the bite of an infected Aedes aegypti mosquito.
Q2. How long does it take to recover from dengue?
👉 Most people recover in about 1–2 weeks with proper rest, fluids, and medical care. Severe cases may take longer.
Q3. What is the danger sign of severe dengue?
👉 Warning signs include bleeding gums, nosebleeds, severe stomach pain, difficulty breathing, or a sudden drop in platelets. These require immediate hospitalization.
Q4. Can papaya leaf juice cure dengue?
👉 Papaya leaf juice is often suggested as a home remedy to improve platelet count, but there is no scientific evidence that it cures dengue. Medical treatment is still necessary.
Q5. When should I see a doctor for fever?
👉 If you have a high fever lasting more than 2 days, along with body pain, rashes, or vomiting, visit a doctor immediately to rule out dengue.
3 thoughts on “Dengue: Symptoms, Causes, Precautions and Treatment”